
Shock Absorbers
Steering & Suspension
The Steering system is a mechanism that enables the driver to guide and direct the vehicle in a chosen direction.
Suspension is the term given to the system of components, springs, shock absorbers and linkages that connects a vehicle to the road surface via the wheels and tyres.
Suspension systems serve a dual purpose — contributing to the car's road holding/handling and braking for good active safety and driving pleasure, and keeping vehicle occupants comfortable and reasonably well isolated from road noise, bumps, and vibrations.
These goals are generally at odds, so the tuning of suspensions involves finding the right compromise. It is important for the suspension to keep the wheels in contact with the road surface as much as possible, because all the forces acting on the vehicle do so through the contact patches of the tyres. The suspension also protects the vehicle itself and any cargo or luggage from damage and wear. The design of front and rear suspension of a car may be different but the following diagrams show a common type of system.
Front Suspension: 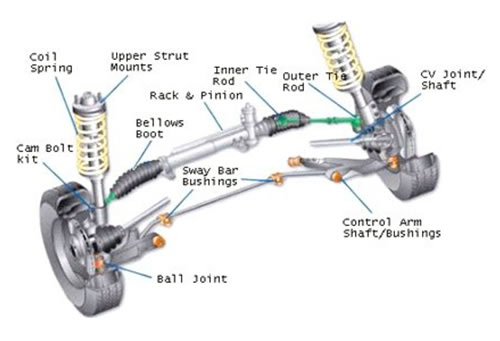
The steering wheel is connected to the rack and pinion system, which moves the wheels right and left via the inner and outer tie rods. These are connected using a track rod end;
The track rod ends are adjusted to ensure the wheels are perfectly aligned (“Tracking”) and that tyre wear is minimised. The track rod end is a common wear item and simple to replace.
A CV joint (constant velocity joint) is part of a drive shaft (the shaft that attaches to a car's transmission at one end and the wheel at the other). CV joints are designed to be able to bend in any direction while continuing to turn the drive wheels at a constant velocity. CV joints are mainly used in the drive shafts of front wheel drive cars.
Due to bumps and uneven surfaces in the road, a car's wheels tend to move up and down continuously while driving down the road; as a result, drive shafts cannot be made up of a solid shaft. The CV joint is used in front wheel drive cars because of its ability to maintain a constant drive force to the wheels despite the many different kinds of movements in the front end of the car. The CV joint is often used in rear wheel drive and four-wheel drive cars too. CV joints should be checked regularly and may need replacing as a car ages.
CV Boot
A CV joint is covered with a bulbous rubber boot that can deteriorate over time. When a CV boot cracks or tears open, the CV joint is exposed to the elements, which will quickly damage the joint. If the CV axles are inspected periodically, torn boots can be replaced as needed, potentially extending the life of the joints. If torn boots are left unattended, the joint or the entire axle may soon need to be replaced.
Front Suspension: 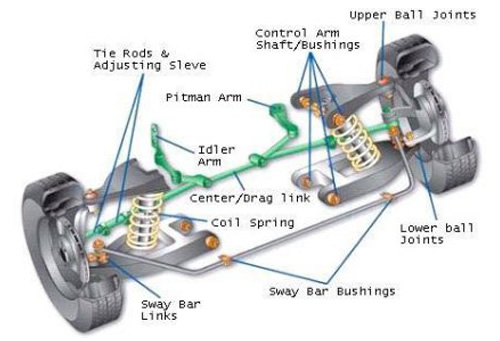
Springs & Shock Absorbers
Springs and Shock absorbers form part of your vehicle's suspension system designed to reduce the effect of bumps and vibrations from road surfaces, providing you with a more comfortable ride. A good suspension system also helps to maintain vehicle stability and handling as well as helping to reduce your braking distance.
How it Works
When a spring is compressed and then released, the energy within the spring causes it to continue to flex up and down before it settles to its original shape. Going over a bump in your car compresses the springs, so the car would also continue to bounce up and down making the car difficult to control. The effect of the shock absorber is to dampen the spring's natural reaction to bounce.
Shock absorbers are filled with hydraulic fluid or gas. When the shock absorber is compressed, this fluid is forced by a piston through a small hole in the shock absorber cylinder and into the other end of the unit. The design prevents this action happening quickly, so the spring is restricted from continuing to bounce, helping to keep all four tyres in good contact with the road surface.
Replacing Springs & Shocks
It can be difficult to recognise a problem with your suspension system because loss of performance occurs gradually over a period of time.
The spring works in an extremely harsh environment and over a mileage of 50,000 miles can move in excess of 500 million times. This leads to sagging or actual snapping. Poorly maintained roads and the prevalence of speed bumps has significantly increased the failure rates of springs in recent years.
To test your shock absorbers try this simple 'bounce' test. Press down on one corner of your car and let go. Count the number of bounces before the car comes to rest. If the car bounces even twice, your shock absorbers could be faulty and need to be checked.
Any suspension fault has a negative effect on your vehicles handling and safety characteristics and leads to premature tyre wear so it is always advisable to seek professional advice.
Our National Tyres and Autocare technicians can arrange this for you – call in at one of our branches (locate your nearest centre).
Suspension Arm
A suspension arm is designed to be attached to a vehicle's chassis; support the wheel hub and allow the suspension to move through its normal range of movement. The loadings on this component are immense and it has to work in extremes of heat, cold and extreme road conditions; a real 'hostile' environment!
Bushes
To connect the various metal components together and allow them to move in a smooth and controlled manner a bushing is used. In vehicle suspension systems, this can be synthetic rubber or polyurethane and separates the faces of two metal objects while allowing a certain amount of movement. This movement allows the suspension parts to move freely, for example, when traveling over a large bump, while minimizing transmission of noise and small vibrations through to the chassis of the vehicle. A rubber bushing may also be described as a flexible mounting or anti vibration mounting.
As you can see a vehicle's steering and suspension system is a complex piece of engineering made up of many components that work together to maintain a safe, controlled and comfortable ride by ensuring maximum Steering, Stability & Stopping for your vehicle.
Due to the harsh environment in which this system operates it is essential that it is checked and maintained on a regular basis.
Should you need to replace any of your vehicle's steering or suspension components, whether it be CV Joints, CV Boot Kits, Drive Shafts, Hub Bearing Kits, Road springs, Shock Absorbers, Steering Racks, Bushes, Tie Rod Ends or Ball Joints just contact your nearest National Tyres and Autocare branch on the number at the top of this page.


 Sign up for SPECIAL OFFERS
Sign up for SPECIAL OFFERS
